Digital Electronics - Counters
Exercise : Counters - Filling the Blanks
- Counters - General Questions
- Counters - True or False
- Counters - Filling the Blanks
16.
In order to check the CLR function of a counter, ________.
17.
The circuit shown below is used for ________, and for the inputs shown, the DATA output will be ________.
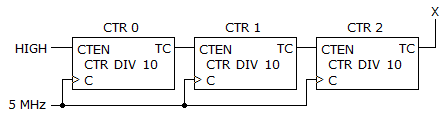
18.
________ is the output frequency of the counter shown below.
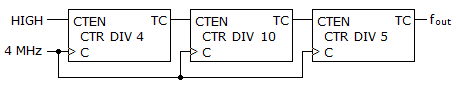
19.
An asynchronous binary up counter, made from a series of leading edge-triggered flip-flops, can be changed to a down counter by ________.
20.
A 4-bit binary up counter has an input clock frequency of 20 kHz. The frequency of the most significant bit is ________.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers
 instead of Q)
instead of Q)