Chemical Engineering - Chemical Reaction Engineering - Discussion
Discussion Forum : Chemical Reaction Engineering - Section 4 (Q.No. 41)
41.
Second order consecutive irreversible reactions 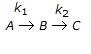 were carried out in a constant volume isothermal batch reactor with different initial feed compositions. Reactor temperature was same in all the cases. In experiments where the ratio of concentration of B to that of A in the initial feed was less than 0.5, the concentration of B increased first, reached a maximum and then declined with time. However, for all experiments where this concentration ratio was 0.5 or above, concentration of B decreased monotonically with time right from the beginning. What is the ratio of the two rate constants (k1/k2)?
were carried out in a constant volume isothermal batch reactor with different initial feed compositions. Reactor temperature was same in all the cases. In experiments where the ratio of concentration of B to that of A in the initial feed was less than 0.5, the concentration of B increased first, reached a maximum and then declined with time. However, for all experiments where this concentration ratio was 0.5 or above, concentration of B decreased monotonically with time right from the beginning. What is the ratio of the two rate constants (k1/k2)?
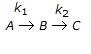 were carried out in a constant volume isothermal batch reactor with different initial feed compositions. Reactor temperature was same in all the cases. In experiments where the ratio of concentration of B to that of A in the initial feed was less than 0.5, the concentration of B increased first, reached a maximum and then declined with time. However, for all experiments where this concentration ratio was 0.5 or above, concentration of B decreased monotonically with time right from the beginning. What is the ratio of the two rate constants (k1/k2)?
were carried out in a constant volume isothermal batch reactor with different initial feed compositions. Reactor temperature was same in all the cases. In experiments where the ratio of concentration of B to that of A in the initial feed was less than 0.5, the concentration of B increased first, reached a maximum and then declined with time. However, for all experiments where this concentration ratio was 0.5 or above, concentration of B decreased monotonically with time right from the beginning. What is the ratio of the two rate constants (k1/k2)?Discussion:
4 comments Page 1 of 1.
Milap said:
2 years ago
2nd order reaction.
-dCb/dt = k2Cb^2 - k1Ca^2.
At 0.5 ratio -dCb/dt = 0.
Therefore by solving above eqn will get k1/k2 = (Cb/Ca)^2 = (0.5)^2 = 1/4.
-dCb/dt = k2Cb^2 - k1Ca^2.
At 0.5 ratio -dCb/dt = 0.
Therefore by solving above eqn will get k1/k2 = (Cb/Ca)^2 = (0.5)^2 = 1/4.
(5)
Zahraa ALjoubori said:
4 years ago
CB/CA = 0.5,
So, CB = 0.5 CA.
-rA = k1CA
-rB = k2CB-K1CA. = 0.5 k2CA-K1CA.
when -rA=-rB.
k1CA = 0.5 k2CA-K1CA.
2 k1CA = 0.5 k2CA.
Then k1/k2=0.5/2 = 1/4.
So, CB = 0.5 CA.
-rA = k1CA
-rB = k2CB-K1CA. = 0.5 k2CA-K1CA.
when -rA=-rB.
k1CA = 0.5 k2CA-K1CA.
2 k1CA = 0.5 k2CA.
Then k1/k2=0.5/2 = 1/4.
(1)
Gautam said:
7 years ago
-rA=k1CA & -rB=k2CB-K1CA.
when -rA=-rB.
then k1/k2=1/4.
when -rA=-rB.
then k1/k2=1/4.
(1)
Pavani said:
9 years ago
Can anyone explain this?
Post your comments here:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers