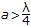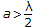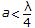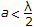Online Electronics and Communication Engineering Test - Microwave Communication Test
- This is a FREE online test. Beware of scammers who ask for money to attend this test.
- Total number of questions: 20.
- Time allotted: 30 minutes.
- Each question carries 1 mark; there are no negative marks.
- DO NOT refresh the page.
- All the best!
Marks : 2/20
Test Review : View answers and explanation for this test.
They are used in all the devices.
Assertion (A): The phenomenon of differential mobility is called transferred electron effect.
Reason (R): GaAs exhibits transferred electron effect.
A Gunn diode uses GaAs which has a negative differential mobility, i.e., a decrease in carrier velocity with increase in electric field.
This effects is called transferred electron effect. The impedance of a Gunn diode is tens of ohms.
A Gunn diode oscillator has a resonant cavity, an arrangement to couple Gunn diode to cavity, biasing arrangement for Gunn diode and arrangement to couple RF power to load.
Applications of Gunn diode oscillator include continuous wave radar, pulsed radar and microwave receivers.
It is somewhat similar to TWT and can deliver microwave power over a wide frequency band.
It has an electron gun and a helix structure. However the interaction between electron beam and RF wave is different than in TWT.
The growing RF wave travels in opposite direction to the electron beam.
The frequency of wave can be changed by changing the voltage which controls the beam velocity.
Moreover the amplitude of oscillations can be decreased continuously to zero by changing the beam current.
It features are:
1. Frequency range - 1 GHz to 1000 GHz.
2. Power output - 10 mV to 150 mW (continuous wave) 250kW (pulsed).
It is used as signal source in transmitters and instruments.
Assertion (A): The condition of minimum distortion in a transmission line is L = RC/G.
Reason (R): Line loading means addition of inductance to satisfy the condition L = RC/G.
Oscillator circuits using vacuum tubes (triodes, pentodes) have the following limitations at very high frequencies (microwave region).
The stray capacitances and inductances become important and affect the operation of the circuit.
At low frequencies the transit time between cathode and anode is a small fraction of period of oscillation.
However, at microwave frequencies this transit time becomes comparable to time period of oscillations.
Double stub is useful for matching over a range of frequencies.
Range of radar is proportional to antenna diameter.
0.054 x 8.68 = 0.47 dB/m.
It is a forward wave because as t increases, x increases.
Some applications require dual polarization capability. Circular waveguide has this capability.
These analysis uses cylindrical coordinates.
In circular waveguide TE11 mode has the lowest cut off frequency and is the dominant mode.
If D is diameter of waveguide
λc = 1.706 D for TE11 mode
λc = 1.029 D for TE21 mode
λc = 0.82 D for TE01 mode
λc = 1.306 D for TM01 mode.

A Klystron is a vacuum tube used for generation/amplification of microwaves.
An electron beam is produced by oxide coated indirectly heated cathode and is focussed and accelerated by focussing electrode.
This beam is transmitted through a glass tube. The input cavity where the beam enters the glass tube is called buncher.
As electrons move ahead they see an accelerating field for half cycle and retarding field for the other half cycle.
Therefore, some electrons are accelerated and some are retarded. This process is called velocity modulation.
The velocity modulation causes bunching of electrons. This bunching effect converts velocity modulation into density modulation of beam.
The input is fed at buncher cavity and output is taken at catcher cavity.
In a two cavity klystron only buncher and catcher cavity are used. In multi cavity klystron one or more intermediate cavities are also used.
The features of a multicavity klystron are :
1. Frequency range - 0.25 GHz to 100 GHz
2. Power output - 10 kW to several hundred kW
3. Power gain - 60 dB (nominal value)
4. Efficiency - about 40%.
A multicavity klystron is used in UHF TV transmitters, Radar transmitter and satellite communication.
Assertion (A): For a reciprocal microwave junction the S matrix is symmetrical.
Reason (R): In a symmetrical matrix Sij = Sji.
Assertion (A): Hollow waveguides are frequently used as transmission lines at microwave frequencies.
Reason (R): Waveguide has high power handling capacity, low loss and simple structure.
Assertion (A): In rectangular waveguide TE01 mode is just TE10 mode rotated by 90°.
Reason (R): When a rectangular waveguide is rotated by 90°, the broad and narrow dimensions get interchanged.