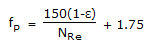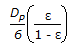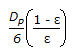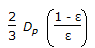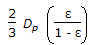Online Chemical Engineering Test - Fluid Mechanics Test 1
Instruction:
- This is a FREE online test. Beware of scammers who ask for money to attend this test.
- Total number of questions: 20.
- Time allotted: 30 minutes.
- Each question carries 1 mark; there are no negative marks.
- DO NOT refresh the page.
- All the best!
Marks : 2/20
Total number of questions
20
Number of answered questions
0
Number of unanswered questions
20
Test Review : View answers and explanation for this test.
1.
The head loss in turbulent flow in a pipe varies
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
2.
The drag co-efficient for a bacterium moving in water at 1 mm/s, will be of the following order of magnitude (assume size of the bacterium to be 1 micron and kinematic viscosity of water to be 10-6m2/s).
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
3.
For the free settling of a spherical particle through a fluid, the slope of, CD-log NRe , plot is
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
4.
Hydraulic intensifier is used for increasing the
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
5.
Pick out the Kozney-Karman equation (valid for low NRe) for fluid flow through a packed bed of solids.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
6.
Transition length for a turbulent fluid entering into a pipe is around __________ times the pipe diameter.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
7.
Pascal's law is valid, only when the fluid is
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
8.
One dimensional fluid flow implies the
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
9.
The discharge through a venturimeter depends upon
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
10.
Gradually varied flow in open channel is a/an __________ flow.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
11.
The pressure and power requirement of a gas fan at constant speed & capacity varies __________ the gas density.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
12.
At low Reynolds number
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
13.
Buckingham-π theorem states that in any physical problem including 'n' quantities having 'm' diamensions, the quantities can be arranged into __________ independent dimensionless parameters.
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
14.
Pressure difference between two points in vessels, pipelines or in two different pipelines can be measured by a differential manometer. The pressure difference measured as the mm of water coloumn in case of mercury-water, differential manometer is equal to (where, H = difference in height of mercury column in mm).
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
15.
What is the ratio of displacement thickness to nominal thickness for a linear distribution of velocity in the boundary layer on a flat plate ?
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
16.
If three pipes of different diameters, lengths & friction factors are connected in parallel, then (where, Q = flow rate, V= fluid velocity f = friction factor).
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
17.
Hydraulic mean radius for flow through packed bed of spherical particle of size, 'Dp, with porosity 'ε' is
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
18.
A gas
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
19.
Slugging occurs in a fluidised bed, if the bed is
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
20.
The Reynolds number for an ideal fluid flow is
Your Answer: Option
(Not Answered)
Correct Answer: Option
Discuss about this problem : Discuss in Forum
Learn more problems on : Fluid Mechanics
*** END OF THE TEST ***
Time Left: 00:29:56
Post your test result / feedback here:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers