Engineering Mechanics - PKRB: Impulse and Momentum
Why should I learn to solve Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "PKRB: Impulse and Momentum"?
Learn and practise solving Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "PKRB: Impulse and Momentum" to enhance your skills so that you can clear interviews, competitive examinations, and various entrance tests (CAT, GATE, GRE, MAT, bank exams, railway exams, etc.) with full confidence.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "PKRB: Impulse and Momentum"?
IndiaBIX provides you with numerous Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "PKRB: Impulse and Momentum" along with fully solved examples and detailed explanations that will be easy to understand.
Where can I get the Engineering Mechanics section on "PKRB: Impulse and Momentum" MCQ-type interview questions and answers (objective type, multiple choice)?
Here you can find multiple-choice Engineering Mechanics questions and answers based on "PKRB: Impulse and Momentum" for your placement interviews and competitive exams. Objective-type and true-or-false-type questions are given too.
How do I download the Engineering Mechanics questions and answers section on "PKRB: Impulse and Momentum" in PDF format?
You can download the Engineering Mechanics quiz questions and answers section on "PKRB: Impulse and Momentum" as PDF files or eBooks.
How do I solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "PKRB: Impulse and Momentum"?
You can easily solve Engineering Mechanics quiz problems based on "PKRB: Impulse and Momentum" by practising the given exercises, including shortcuts and tricks.
- PKRB: Impulse and Momentum - General Questions
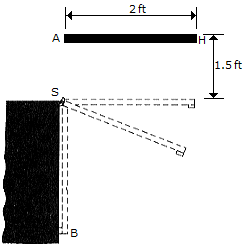
The uniform rod AB has a weight of 3 lb and is released from rest without rotating from the position shown. As it falls, the end A strikes a hook S, which provides a permanent connection. Determine the speed at which the other end B strikes the wall at C.
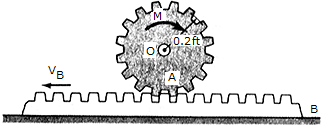
Gear A has a weight of 1.5 lb, a radius of 0.2 ft, and a radius of gyration of ko = 0.13ft. The coefficient of friction between the gear rack B and the horizontal surface is  = 0.3. If the rack has a weight of 0.8 lb and is initially sliding to the left with a velocity of (vB)2 = 8 ft/s to the left. Neglect friction between the rack and the gear and assume that the gear exerts only a horizontal force on the rack.
= 0.3. If the rack has a weight of 0.8 lb and is initially sliding to the left with a velocity of (vB)2 = 8 ft/s to the left. Neglect friction between the rack and the gear and assume that the gear exerts only a horizontal force on the rack.
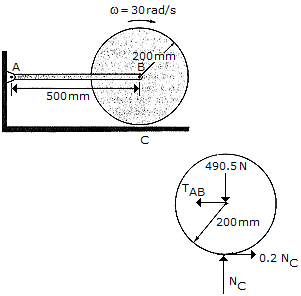
The 50-kg cylinder has an angular velocity of 30 rad/s when it is brought into contact with the horizontal surface at C. If the coefficient of friction is  c = 0.2, determine how long it takes for the cylinder to stop spinning. What force is developed at the pin A during this time? The axis of the cylinder is connected to two symmetrical links. (Only AB is shown.) For the computation, neglect the weight of the links.
c = 0.2, determine how long it takes for the cylinder to stop spinning. What force is developed at the pin A during this time? The axis of the cylinder is connected to two symmetrical links. (Only AB is shown.) For the computation, neglect the weight of the links.
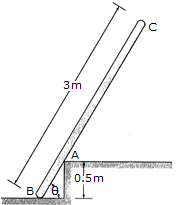
The uniform pole has a mass of 15 kg and falls from rest when  = 90° until it strikes the edge at A,
= 90° until it strikes the edge at A,  = 60°. If the pole then begins to pivot about this point after contact, determine the pole's angular velocity just after the impact. Assume that the pole does not slip at B as it falls until it strikes A.
= 60°. If the pole then begins to pivot about this point after contact, determine the pole's angular velocity just after the impact. Assume that the pole does not slip at B as it falls until it strikes A.
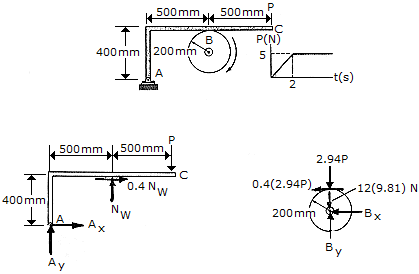
The 12-kg disk has an angular velocity of  = 20 rad/s. If the brake ABC is applied such that the magnitude of force P varies with time as shown, determine the time needed to stop the disk. The coefficient of friction at B is
= 20 rad/s. If the brake ABC is applied such that the magnitude of force P varies with time as shown, determine the time needed to stop the disk. The coefficient of friction at B is  = 0.4.
= 0.4.