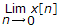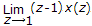Electronics and Communication Engineering - Signals and Systems
Exercise : Signals and Systems - Section 5
- Signals and Systems - Section 1
- Signals and Systems - Section 2
- Signals and Systems - Section 3
- Signals and Systems - Section 4
- Signals and Systems - Section 5
- Signals and Systems - Section 6
- Signals and Systems - Section 7
- Signals and Systems - Section 8
- Signals and Systems - Section 9
- Signals and Systems - Section 10
26.
X and Y are two random variable and Z = X + Y. Let σx2, σy2 and σz2 be variance of X, Y and Z. Then
27.
Consider the following sets of values of E, R and C for the circuit in the given figure.
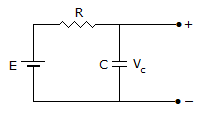
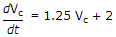 is valid?
is valid?

- 2 V, 1 Ω, 1.25 F
- 1.6 V, 0.8 Ω, 1 F
- 1.6 V, 1 Ω, 0.8 F
- 2 V, 1.25 Ω, 1 F
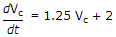 is valid?
is valid?28.
Assertion (A): The conditions under which it is possible to write Fourier series of a periodic function are called Drichlet conditions.
Reason (R): If f(t) = - f(- t), it is refereed to as odd symmetry.
29.
Initial value theroem for sequence x[n] is
30.
L[c1f1(t) + c2f2(t)] =
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers