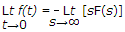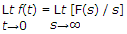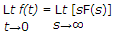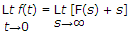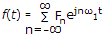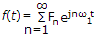Electronics and Communication Engineering - Signals and Systems
Exercise : Signals and Systems - Section 4
- Signals and Systems - Section 1
- Signals and Systems - Section 2
- Signals and Systems - Section 3
- Signals and Systems - Section 4
- Signals and Systems - Section 5
- Signals and Systems - Section 6
- Signals and Systems - Section 7
- Signals and Systems - Section 8
- Signals and Systems - Section 9
- Signals and Systems - Section 10
41.
The initial value theorem is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
£f(t) = 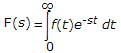
£-1F(s) = f(t)
£[a f1(t) + bf2(t)] = aF1(s) + bF2(s)
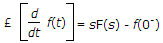
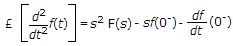
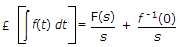
where 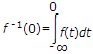
£[f(t - T)] = e-sT F(s)
£[e-at f(t)] = F(s + a)
Initial value theorem 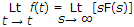
Final value theroem 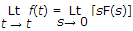
Convolution Integral 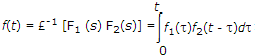
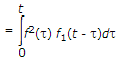
where t is dummy variable for t.
42.
Assertion (A): The rms value of v = 1 + sin ωt is 1.5
Reason (R): If i = I0 + I1m sin ω1t + I3m sin 3ω1t, then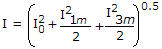
Answer: Option
Explanation:
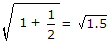 .
.
43.
The exponential form of Fourier series is
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Both a and b are exactly the same except the way of writing.
44.
Principle of superposition is applicable to
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Superposition is valid if response is linearly related to cause.
45.
The range of value "a" for which system will be stable. If impulse response of DT system is = an ∪[n]
Answer: Option
Explanation:
Given n(n) = an ∪(n)
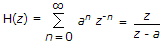
ROC is |z| > a open the mod function
when z > 0
⇒ z > a
z < 0 ⇒ - z > a or ⇒ z < - a
For stability ROC must include unit circle, so
|z| > a or - a < z < + a or -1 < a < + 1.
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers