Aptitude - Alligation or Mixture - Discussion
Discussion Forum : Alligation or Mixture - General Questions (Q.No. 12)
12.
In what ratio must a grocer mix two varieties of tea worth Rs. 60 a kg and Rs. 65 a kg so that by selling the mixture at Rs. 68.20 a kg he may gain 10%?
Answer: Option
Explanation:
S.P. of 1 kg of the mixture = Rs. 68.20, Gain = 10%.
| C.P. of 1 kg of the mixture = Rs. |  |
100 | x 68.20 | 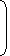 |
= Rs. 62. |
| 110 |
By the rule of alligation, we have:
| Cost of 1 kg tea of 1st kind. Cost of 1 kg tea of 2nd kind. | ||
| Rs. 60 | Mean Price Rs. 62 | Rs. 65 |
| 3 | 2 | |
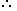 Required ratio = 3 : 2.
Required ratio = 3 : 2.
Discussion:
23 comments Page 2 of 3.
Sam said:
9 years ago
I can't get it. Please explain.
(1)
Nitesh said:
9 years ago
There will be profit, hence less price object will be in more than other.
Hence, 3 : 2 only one option.
Hence, 3 : 2 only one option.
(1)
Nitin said:
9 years ago
I think the ratio should be 2:3 not 3:2.
Correct me if I am wrong.
Correct me if I am wrong.
Krishna said:
1 decade ago
It was said that there was 10% profit for selling a K.G of mixture for 68.20 rs.
But we generally know for any good of C.P 100 rs, S.P of that good becomes 110 rs in case of 10% profit.
Now, S.P - C.P.
110 - 100 => (100*68.20)/110 = 62.
68. 20 - ?
Now, by using the equation.
(60*(x)+65(y))/x+y = 62.
On substituting values from options we get x=3 y=2, ratio becomes 3:2.
But we generally know for any good of C.P 100 rs, S.P of that good becomes 110 rs in case of 10% profit.
Now, S.P - C.P.
110 - 100 => (100*68.20)/110 = 62.
68. 20 - ?
Now, by using the equation.
(60*(x)+65(y))/x+y = 62.
On substituting values from options we get x=3 y=2, ratio becomes 3:2.
Sumanth geras said:
1 decade ago
Easy method applicable for all these kinds of problems.
(quantity 1*price 1+quantity 2*price 2)/quantity 1+quantity 2 = mean quantity.
Since it is given that he got 10 % profit so this 10% is for additional money which is added to mean value obtained (i.e 10% of 68.20 is 62 approximately).
(60(x)+65(y))/x+y = 62. If you solve it you get 3:2.
(quantity 1*price 1+quantity 2*price 2)/quantity 1+quantity 2 = mean quantity.
Since it is given that he got 10 % profit so this 10% is for additional money which is added to mean value obtained (i.e 10% of 68.20 is 62 approximately).
(60(x)+65(y))/x+y = 62. If you solve it you get 3:2.
Muna said:
1 decade ago
How to find out mean price?
Usha said:
1 decade ago
Can any one explain how 110/100*68.20 = Rs. 62?
Rishabh said:
1 decade ago
As we know %gain means %gain over CP =SP - CP.
Hence,10% * CP =SP - CP.
Upon solving you will get CP=100/110 * SP.
Hence,10% * CP =SP - CP.
Upon solving you will get CP=100/110 * SP.
Swejal said:
1 decade ago
Can someone please explain the 2nd step i.e C.P of 1 kg.
Pandia said:
1 decade ago
60*3+65*2 = 180+130.
310 this total 5 kg rate 3 60 kg and 2 65kg.
So one kg 310/5 = 62 this is cost price so the ratio of mixture is 3:2.
310 this total 5 kg rate 3 60 kg and 2 65kg.
So one kg 310/5 = 62 this is cost price so the ratio of mixture is 3:2.
Post your comments here:
Quick links
Quantitative Aptitude
Verbal (English)
Reasoning
Programming
Interview
Placement Papers